geography of iran
Iran, situated in the heart of the vast Southwestern Asian plateau, has for centuries served as a bridge connecting East and West. With its ancient history and civilization, the country lies at the crossroads of major trade and cultural routes. Its geography has always played a decisive role in shaping regional and global developments. Beyond its size and abundant resources, Iran’s strategic location among seas, mountains, and deserts has made it a vital link between civilizations and nations.
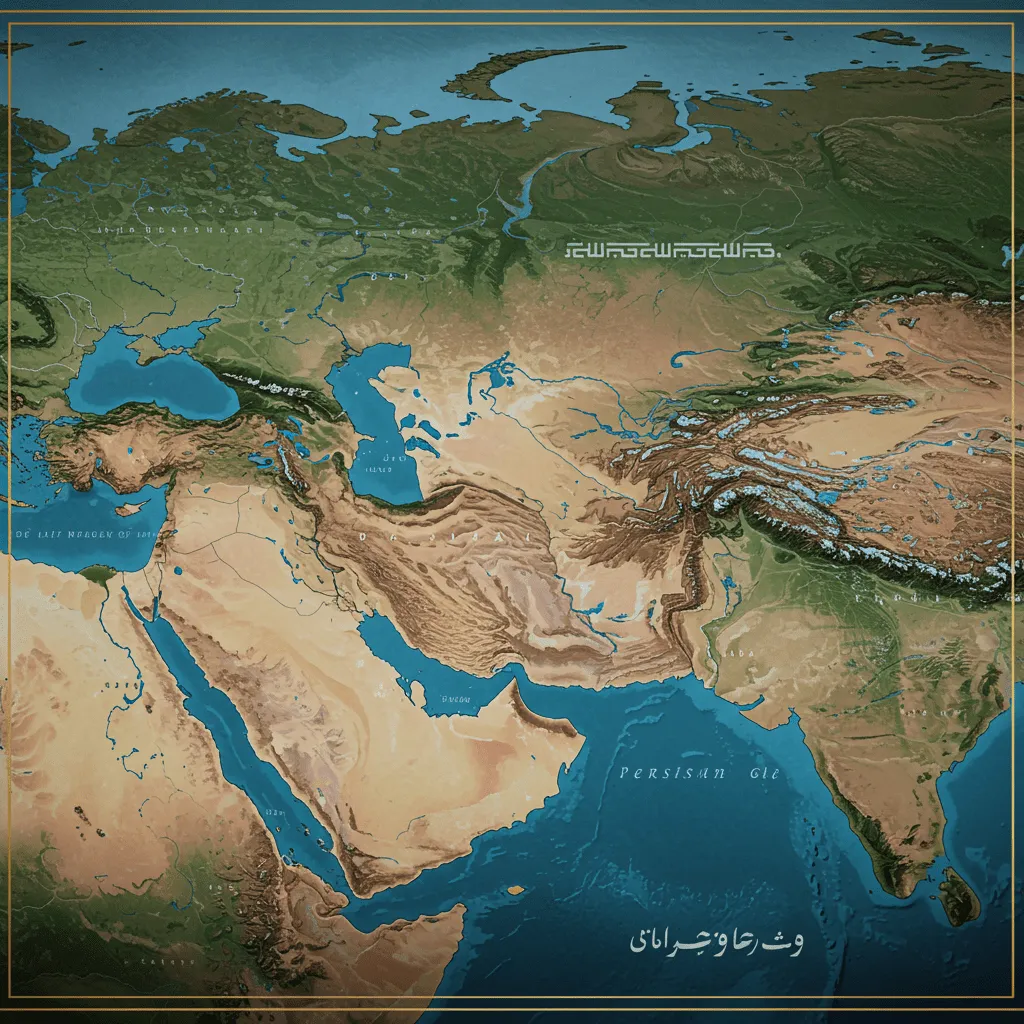
Geography and Borders
Covering nearly 1.65 million square kilometers, Iran ranks as the 18th largest country in the world. It borders the Caspian Sea to the north and the Persian Gulf and the Sea of Oman to the south. On land, Iran shares frontiers with Afghanistan, Pakistan, Turkey, Iraq, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Armenia. This geographical position makes Iran a central hub connecting Central Asia, the Caucasus, the Indian Subcontinent, and the Middle East. The Alborz Mountains in the north and the Zagros Mountains in the west, alongside vast central deserts, give the country a uniquely diverse landscape.
Strategic and Transit Importance
Iran is located along one of the world’s most critical trade corridors. Its position between the Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf makes it a vital route for energy and international trade. Projects such as the North–South Transport Corridor and Iran’s connection to the Silk Road routes have strengthened its role in the global economy. Southern ports like Bandar Abbas and Chabahar serve as key gateways for Central Asian countries to access open waters.
Regional Political and Security Role
Due to its geopolitical location, Iran plays an influential role in the security dynamics of the Middle East and Central Asia. Its proximity to sensitive regions makes it an important actor in regional political and security developments. Iran’s participation in regional organizations and initiatives highlights its capacity to act as a proactive partner in economic, security, and cultural cooperation.
Natural Resources and Economic Geography
In addition to its strategic location, Iran holds vast reserves of energy. Its rich oil and natural gas resources, combined with its transit routes, make Iran one of the key players in global energy markets. This combination strengthens its position as a central country in regional energy supply networks.
Conclusion
Iran’s geographical position not only shapes its diverse natural and climatic features but also defines its regional and global role. Acting as a bridge between civilizations and a strategic market for economic, political, and cultural cooperation, Iran’s future will undoubtedly remain central to regional geopolitics.

